Actuator Cable Disengagement Mechanism
Compact service mechanism for jam recovery and latch release under strict packaging and load constraints
Overview
Timeframe: 2024-2025
Institution: University of Toronto - MIE442 (Mechanical Design)
Team Size: 5 members (Sam Bahrami, Kelvin Cao, Clive Fellows, Mo Taban, Batu Tibet)
Role: Mechanical Design and Structural Validation Engineer
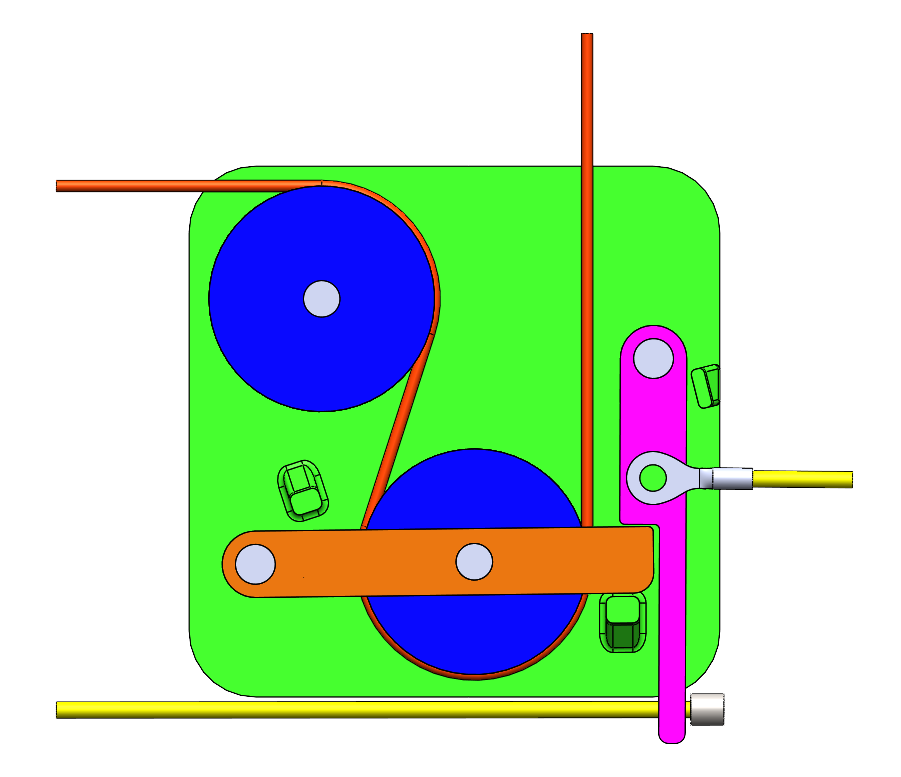
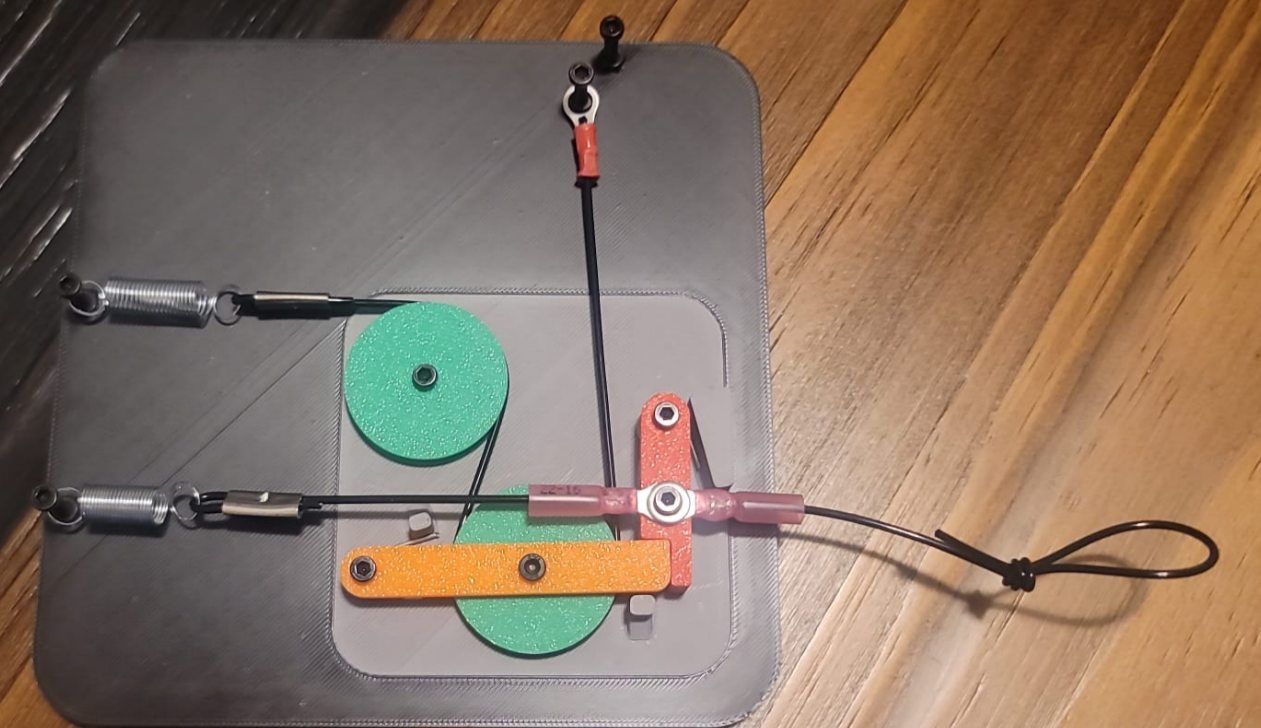
Designed a manual service mechanism that slackens a jammed actuator cable and releases the latch from one pull while fitting within an 80 x 80 x 30 mm envelope and holding a 2.0 safety factor.
The Problem
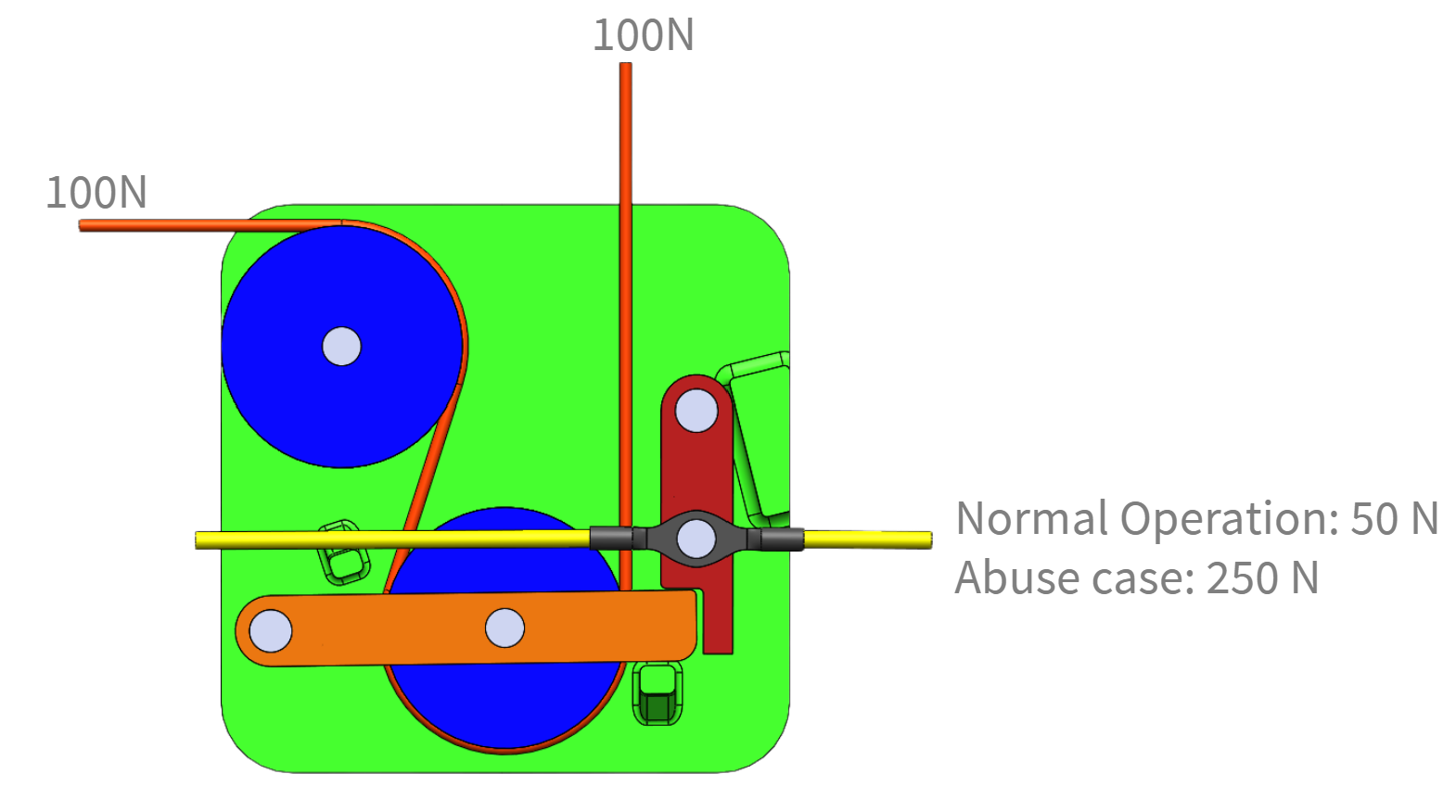
Stalled actuators keep the latch locked by holding cable tension. The mechanism needed to create slack and release the latch with a single input, stay under 50 N pull force, and survive 250 N abuse loads.
Constraints
- 80 x 80 x 30 mm package
- Single 50 N manual pull
- 250 N abuse load with ≥2.0 safety factor
- Repeated service cycles and elevated temperature
- Both slack generation and latch release from one motion
Solution
I led concept and validation work:
- Lever and pulley layout that generates slack and triggers the latch in the same stroke
- Service lever geometry sized for 50 N input and hard stops for repeatability
- Steel pins with polymer housings and torsion springs for reset and durability
- Compact stack-up optimized for manufacturability and tolerance control
Analysis
- Free body and contact stress checks on service, jam, and abuse cases
- Beam and pin stress sizing with Modified Goodman fatigue review
- ANSYS static runs to confirm hand calculations within acceptable agreement
- Iterative geometry tweaks to remove stress concentrations
Tools & Technologies
Design Validation
Results:
- Met the 50 N pull target with margin through mechanical advantage
- Cleared 2.0 safety factor across service and abuse cases
- Validated cyclic life for pins and springs
- Kept the full assembly inside the 80 x 80 x 30 mm volume
Key Learnings
- Hand calculations first made FEA setup faster and more trustworthy.
- Tight packaging forced a cleaner architecture that combined functions.
- Designing for manufacturing early avoided costly geometry changes later.